
- Shandong Microwave Machinery Co.,Ltd.
- To be the Leader of microwave drying and edible oil refining equipments Manufacturer
Home> Company News> Optimization of Angelica Microwave Drying Sterilization Process
- AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Factory AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Phone(Working Time)+86 0531 85064681
- Phone(Nonworking Time)0086-15020017267
- Fax+ 86 0531 85064682
Optimization of Angelica Microwave Drying Sterilization Process
2018-11-27 15:21:33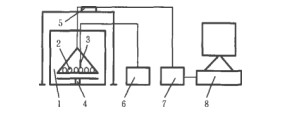
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the optimum technological conditions for the drying and sterilization of Angelica sinensis. Methods: The factors were screened by single factor test and L9 ( 34 ) orthogonal test. The total number of colonies of Angelica sinensis, ferulic acid content and final water content were comprehensively evaluated. Results: The optimal microwave drying and sterilization process parameters of Angelica sinensis was 15% water content of Angelica, microwave power 12 kw, microwave rotation speed 1030 r·s - 1 and sample loading 10 kg·m - 2 .
Conclusion: By optimizing the process of Angelica microwave drying equipment, the loss of ferulic acid, the active ingredient of Angelica sinensis, can be reduced, and the purpose of effective sterilization can also be achieved. The use of improving and improving the quality of products can provide scientific research for the processing and production of Gansu and the national Angelica. in accordance with.
[Key words] microwave drying angelica; process optimization
Angelica is the dry root of Angelica sinensis Angeliasinensis ( Oliv. ) Diel, mainly produced in Gansu County, Sichuan Province and Yunnan Province. Angelica has a high medicinal value and has been highly valued by scholars at home and abroad. Angelica is one of the most commonly used traditional Chinese medicines in the clinic, especially in the gynecological medicine, it has the reputation of “ten and nine return”, and has the functions of blood and blood, regulating menstruation and relieving pain, and relaxing bowel movements.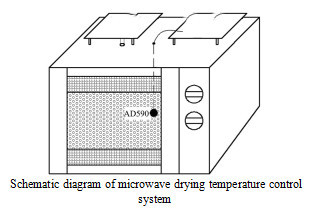
The active constituents of Angelica are mainly volatile oils and organic acid compounds, and the organic acid compounds are mainly ferulic acid. Studies have shown that ferulic acid has various pharmacological effects such as hypolipidemic, antithrombotic, antioxidative, antibacterial and anticancer effects. Therefore, the control of the quality of Angelica sinensis is usually carried out by measuring the content of ferulic acid in Angelica sinensis.
Drying is one of the important factors affecting the quality and clinical function of Chinese herbal medicines. Microwave is a highly penetrating electromagnetic wave with a frequency between 300 and 300 000 MHz. As early as the 1960s, microwaves were used as an energy source for heating, drying, sterilization and medical treatment. Compared with the traditional drying method, the material itself is a heating element during microwave drying, and the direction of heat conduction is consistent with the direction of water diffusion, and has the advantages of fast drying speed, uniform heating, and high drying efficiency.
Therefore, microwave drying technology has been widely applied to the rapid drying of the food industry, wood, ceramic industry, agricultural products and Chinese medicine. The heat source provided by the microwave can directly heat the material, so that the material can be quickly dried and a better drying effect is obtained. For example, He Chunnian et al. studied the effects of various drying techniques (including natural drying, indoor dryness, oven blast drying, vacuum drying and microwave drying) on the total flavonoid content in the leaves of Astragalus membranaceus. The effect of flavonoids is minimal.
In addition, the study also found that microwave drying has the function of sterilization and disinfection, which can prevent mold and insects from being stored during storage, so that the medicine can reach hygienic standards. However, in the production of Chinese herbal medicines, microwave drying is a very complicated process, and there are many factors affecting microwave drying, such as: initial water content of the material, microwave power, heating time, material shape, sample loading and uniform heating. Degree and so on.
Therefore, the choice of process conditions for microwave drying is critical. Therefore, based on the traditional drying process of Angelica sinensis, the effects of water content, microwave power, microwave rotation speed and sample loading on the content of ferulic acid, the total number of colonies and the final moisture content of Angelica sinensis were analyzed by single factor and orthogonal test. The best process combination of angelica microwave drying and sterilization was obtained, in order to provide the basis for the processing and production of the national angelica.
 High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line
High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line
Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line used deformered bar rolling mill production line
used deformered bar rolling mill production line Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line
Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply
Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply