
- Shandong Microwave Machinery Co.,Ltd.
- To be the Leader of microwave drying and edible oil refining equipments Manufacturer
Home> Company News> Effects of Microwave-Hot Air Combined Drying on Processing Quality and Microbial Biomass of High Moisture Rice
- AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Factory AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Phone(Working Time)+86 0531 85064681
- Phone(Nonworking Time)0086-15020017267
- Fax+ 86 0531 85064682
Effects of Microwave-Hot Air Combined Drying on Processing Quality and Microbial Biomass of High Moisture Rice
2019-01-17 14:03:48Absrtact: The microwave drying characteristics of high moisture paddy under different microwave effective power were studied, and the effects of microwave treatment on the processing quality and microbial biomass of paddy were discussed.
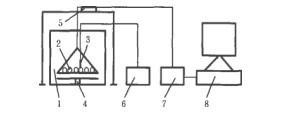
The results showed that under the lower microwave drying equipment (485 W and 927 W), the temperature of paddy increased rapidly and the moisture content decreased slowly in the initial stage of treatment. When the temperature reached 65 C and the moisture content reached 19.7%, the heating rate of paddy decreased, while the water content decreased faster. Increasing microwave power can significantly increase the heating rate and precipitation rate of paddy, but high power microwave drying of paddy is prone to produce scorch phenomenon.
Under the microwave condition of 927 W effective power, the rice can be heated to 60 C in 2 minutes, and the moisture content of the rice can be reduced from 21.58% to 19.96%. After 4 hours of slow-thawing treatment, the bacterial amount on the surface of rice decreased by 3.6 log CFU/mL, and the fungi amount on the surface decreased by 3.3 log CFU/mL. 95% of the fungi in the interior of rice could be sterilized. There was no significant decrease in the roughness and head rice rate (P > 0.05), 83.92% and 68.14% respectively.
Compared with natural ventilation and hot air treatment, the combined treatment of microwave and hot air only takes 20 minutes, and the quality of rice processing is higher, and the germicidal effect is much higher than that of natural ventilation and hot air treatment. Therefore, suitable microwave treatment can significantly shorten the drying time and obtain high quality bactericidal effect on the premise of guaranteeing the processing quality of high moisture paddy, so as to realize rapid and safe storage disposal of high moisture paddy.
Key words: rice microwave drying; microwave radiation; roughness; head rice rate; bacterial quantity; fungus quantity

Rice is one of the most important food crops in the world, and also the main grain reserve in China. At present, the total yield of rice in China has reached 206.43 million tons, of which the yield of Japonica rice accounts for 34%, while that of Jiangsu Province accounts for more than 30% of the total yield of Japonica rice in China. With the improvement of the efficiency of agricultural production mode and the promotion of mechanized harvesting operation, the number of high moisture paddy increased sharply.
However, the existing mechanical drying can not meet the needs of high quality, safety and rapid warehousing of rice, resulting in high moisture rice entering the market circulation and sales. High moisture paddy is susceptible to mildew caused by fungi, which makes the quality of paddy unstable and easy to reduce in storage. Some pathogenic bacteria can produce mycotoxins in rice, which seriously threaten human health.
According to FAO statistics, nearly 3% of the world's food is lost by mildew every year. Hot air drying is the most widely used traditional rice drying technology in industrialization. It is simple to operate and easy to control, but it often causes serious waist bursting, poor taste quality, low sterilization efficiency and high cost. In order to solve the problems of deterioration of high moisture paddy quality and mildew prevention, an efficient, safe and environmentally friendly method is urgently needed.
At present, microwave technology is gradually applied in the fields of food drying, sterilization, insect control and mildew prevention. However, rice is heat sensitive and especially sensitive to temperature. If the heating temperature is too high or the precipitation rate is too fast, there will be a big difference in temperature and moisture between the inside and outside of the paddy, and then there will be waist bursting, which will reduce the quality of the paddy and greatly damage its economic value.
Therefore, it is of great significance to study the lethal effects of different industrial microwave radiation processes on mould and bacteria inside and on the surface of paddy grains, and compare them with natural ventilation and hot air treatment, to analyze the effects of microwave and hot air combined processes on the processing quality of paddy, such as head milled rice rate, and so on, for the safe storage of high moisture paddy.
 High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line
High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line
Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line used deformered bar rolling mill production line
used deformered bar rolling mill production line Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line
Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply
Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply